-
+91 8692846868
-
drmys79@gmail.com
-
Mon: 9:00am to 6:00pm, Fri to Sat: 10:00am - 4:00pm
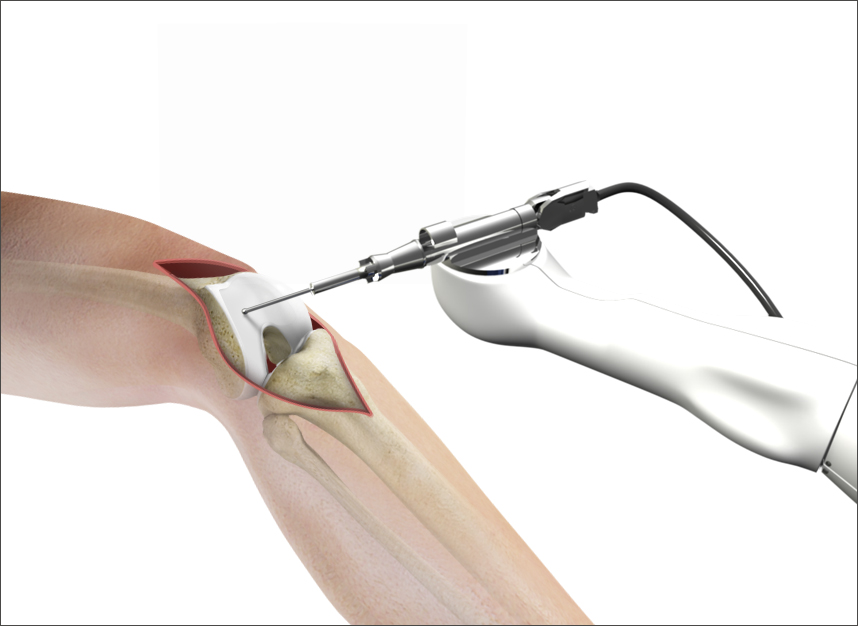
Robotic Knee Replacement
Dr. Manish Sontakke is a certified Robotic knee and Hip replacement surgeon by STRYKER USA.
He is trained in Robotic Total Knee replacement and Partial or Unicondylar Knee Replacement and also Robotic Hip Replacements.
Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty(TKA) is one of the safest and cost-effective procedures performed in orthopedics. With a patient satisfaction rate measured within the range of 75% to 92%, TKA presents a powerful method for pain relief and functional restoration in patients with advanced arthritis when exhausting all of the non-operative options. As technology and surgical procedures develop, surgeons try to improve patient outcomes and satisfaction. Robots present a tool in which surgeons can do surgical procedures while minimizing human error and maximizing operative accuracy.
Robotic TKR uses a preoperative CT scan to create a 3D reconstruction of the original knee. This patient model is then used to calculate the measurement of the femoral and tibial bone resection and select the exact size of the implant.
The aim of TKA is to restore the mechanical axis, restore the joint line, restore balance in flexion and extension gaps, and restore the Q angle for perfect patella tracking. To reach these goals, the preservation of the surrounding soft-tissue is crucial.
Robotic total knee arthroplasty uses certain software to convert anatomical images into a virtual three-dimension reconstruction of joints. The anatomy is usually obtained by requesting pre-operative CT or intraoperative tibia and femur mapping. The surgeons use this model to plan the perfect bone cut, implant positioning, limb alignment, and bone coverage based on the patient’s anatomy. The intraoperative robotic device helps to minimize iatrogenic soft-tissue and bony injury.
Robotic TKA is a technology that uses dynamic referencing to assess knee stability, alignment, and knee range of movement intraoperatively, enabling intraoperative adjustments of bone resection and positioning of the prosthesis. Reduced soft-tissue dissection and muscle injury help reduce the inflammatory response and improve the achievement of physiotherapy goals quickly, such as straight leg raise restoration.
FAQ's
When we talk about “robotic” knee replacements, we’re referring to how the procedure is done – not the type of artificial joint that’s implanted. In other words, you will not have a robotic knee joint after surgery.
Instead, robotic knee replacement is a procedure that uses a robotic technology to improve accuracy and precision during knee replacement. I currently use the MAKO® Knee System by Stryker USA,through which I do Robotic arm assisted knee replacements.
And, if you’re wondering if the robot performs the surgery on its own, the answer is no.
“The robot assists me in performing the surgery – it doesn't do the surgery itself,”
In fact, the role of the robotic assistant is to provide surgeons with real-time information to make sure the new joint is precisely placed based on the patient’s unique anatomy. But while the robot provides a guide for greater precision, your doctor still needs to be a skilled surgeon. That’s why it’s so important to work with an orthopedic surgeon who’s experienced in total knee replacements.
“Fundamentally, a robotic-assisted knee replacement is the same procedure as traditional knee surgery. “The only difference is the technology we use.”
During all knee replacement surgeries, the damaged bone and cartilage is removed from the joint and kneecap before an artificial joint – which is made of metal alloys, high-grade plastics and polymers – is implanted.
Using robotic technology allows doctors to be more precise and accurate when making surgical bone cuts, releasing soft tissue and positioning the implant. This is because doctors have more information to work with.
Before a knee replacement using a robotic-surgical assistant, CT scan of your knees are taken to get detailed information about your specific anatomy. These CT scan is used to plan out the procedure, including the best locations for the surgical cuts and knee implant.
Then, during the procedure, the robotic assistant uses cameras and optical lens tracking to follow the exact position of your leg. The robot provides continuous feedback to your surgeon during your procedure by using infrared cameras and optical trackers to help them make real-time decisions, improve the personalization of the surgery and increase visibility.
“If your leg moves – even just slightly – the robot adjusts so that the surgery is as precise and accurate as possible,”. “We can change the measure of the cuts by as little as one millimeter to achieve exactly what we want.”
If you’re a candidate for a total knee replacement, it’s likely that a robotic-assisted procedure is an option for you.
“Anybody can have a robotic knee surgery,”“But it’s especially good for patients with challenging needs, trauma or prior surgeries to their knees. Surgery in those situations can be very difficult, and I anticipate that the robot would be very helpful.”