-
+91 8692846868
-
drmys79@gmail.com
-
Mon: 9:00am to 6:00pm, Fri to Sat: 10:00am - 4:00pm
complete trauma care
A trauma center (or trauma centre) is a hospital equipped and staffed to provide care for patients suffering from major traumatic injuries such as falls, motor vehicle collisions, or gunshot wounds. A trauma center may also refer to an emergency department (also known as a "casualty department" or "accident and emergency") without the presence of specialized services to care for victims of major trauma.
Trauma surgery is a surgical specialty that utilizes both operative and non-operative management to treat traumatic injuries, typically in an acute setting. Trauma surgeons generally complete residency training in general surgery and often fellowship training in trauma or surgical critical care.

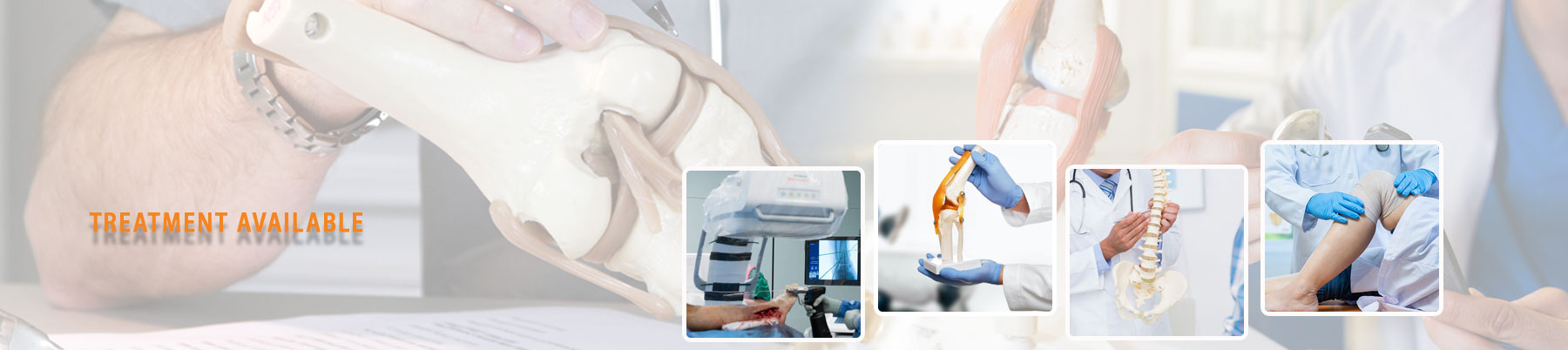
Management of complex Polytrauma limb salvage
Trauma to the extremities is one of the most common injury patterns seen in emergency medical and surgical practice. Optimal outcomes for these patients requires a multidisciplinary approach with oversight by the general or trauma surgeon and care from other specialists including orthopedic, vascular, and plastic surgeons and rehabilitation specialists.
In most instances, a course of limb salvage can be attempted even if the patient has a mangled extremity; however, occasionally, the lower extremity injury is so severe that primary amputation at the initial operation is required to save the patient's life. Complications of surgical treatment for lower severe extremity injury are common; early recognition and treatment are important to minimize morbidity and mortality.
Paediatric trauma
Trauma in children, also known as pediatric trauma, refers to a traumatic injury that happens to an infant, child or adolescent. Because of anatomical and physiological differences between children and adults the care and management of this population differs.
Trauma continues to be the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the paediatric population. In Victoria there are around 2,000 trauma related presentations to the Royal Children’s Hospital, the paediatric Major Trauma Service (MTS), each year either through direct admission or via inter-hospital transfer.

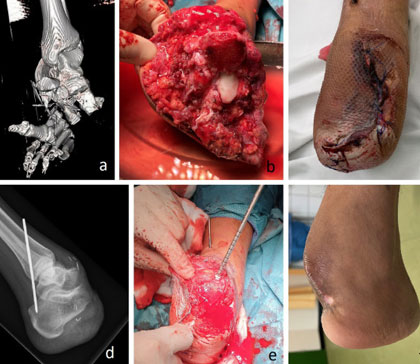
Periprosthetic fractures
Periprosthetic fractures are fractures that occur in association with an orthopaedic implant, most often used for joint arthroplasty or fracture fixation. They are associated with significant morbidity and increased mortality in some cases.
The incidence of periprosthetic fractures appears to be increasing as a result of increasing patient longevity, more demanding activity levels that persist into advanced age for some patients, and as a result of the increasing rate of revision arthroplasty which accompanies increasing patient longevity.
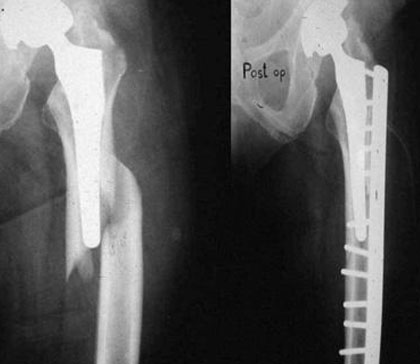
ARTHROSCOPY
Arthroscopy (ahr-THROS-kuh-pee) is a procedure for diagnosing and treating joint problems. A surgeon inserts a narrow tube attached to a fiber-optic video camera through a small incision — about the size of a buttonhole. The view inside your joint is transmitted to a high-definition video monitor.
Arthroscopy allows the surgeon to see inside your joint without making a large incision. Surgeons can even repair some types of joint damage during arthroscopy, with pencil-thin surgical instruments inserted through additional small incisions.
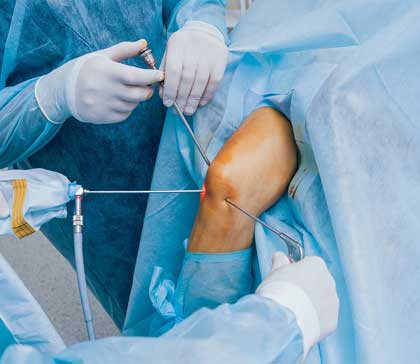
Arthroscopic ACL PCL reconstruction
Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACL reconstruction) is a surgical tissue graft replacement of the anterior cruciate ligament, located in the knee, to restore its function after an injury. The torn ligament can either be removed from the knee (most common), or preserved (where the graft is passed inside the preserved ruptured native ligament) before reconstruction through an arthroscopic procedure.
ACL repair is also a surgical option. This involves repairing the ACL by re-attaching it, instead of performing a reconstruction. Theoretical advantages of repair include faster recovery and a lack of donor site morbidity, but randomised controlled trials and long-term data regarding re-rupture rates using contemporary surgical techniques are lacking.
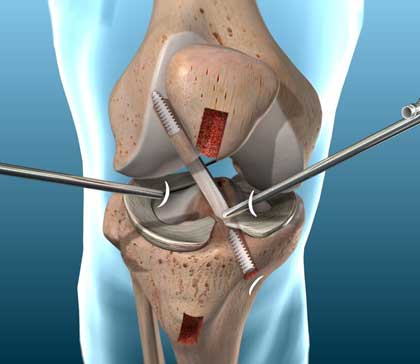
Meniscus repair
Meniscus surgery is an operation to remove or repair a torn meniscus, a piece of cartilage in the knee.
Each knee has two menisci. They are rubbery, C-shaped cushions that serve as shock absorbers in the knee joint. If your meniscus is injured or torn (often called torn cartilage), your healthcare provider may recommend surgery to remove the damaged part or repair it.
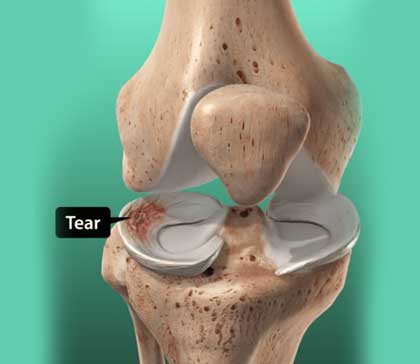
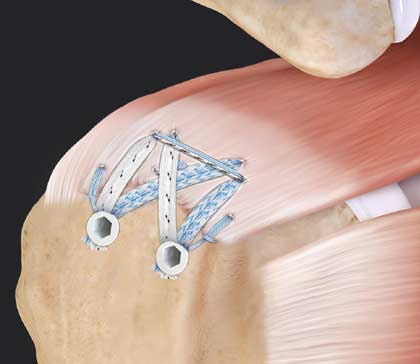
Shoulder arthroscopic Bankarts repair
The shoulder is one of the largest and most complex joints in the human body. The humerus (upper arm bone) and the scapula (shoulder blade) join to form the shoulder joint. It is also referred to as a ball and socket joint and is surrounded by muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
A Bankart lesion is a shoulder injury that occurs due to a labrum tear causing instability and recurrent dislocations of the shoulder joint. Arthroscopic Bankart repair is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed to reattach and tighten the detached labrum within the shoulder joint.
Rotater cuff repair
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that form a cuff over the shoulder joint. These muscles and tendons hold the arm in its joint and help the shoulder joint to move. The tendons can be torn from overuse or injury.
You will likely receive general anesthesia before this surgery. This means you will be asleep and unable to feel pain. Or, you will have regional anesthesia. Your arm and shoulder area will be numbed so that you do not feel any pain. If you receive regional anesthesia, you will also be given medicine to make you very sleepy during the operation.
Surgeries for acute and chronic joint dislocations
The place where two or more bones in the body come together is called a joint. A dislocation occurs when the bones in a joint become separated or knocked out of their usual positions. Any joint in the body can become dislocated. If the joint is partially dislocated, it is called a subluxation.
Dislocations can be very painful and cause the affected joint area to be unsteady or immobile (unable to move). They can also strain or tear the surrounding muscles, nerves, and tendons (tissue that connects the bones at a joint). You should seek medical treatment for a dislocation.